C++ 异常是指在程序运行时发生的特殊情况,比如尝试除以零的操作。
异常提供了一种转移程序控制权的方式。C++
异常处理涉及到三个关键字:try、catch、throw。
throw: 当问题出现时,程序会抛出一个异常。这是通过使用 throw
关键字来完成的。
catch: 在您想要处理问题的地方,通过异常处理程序捕获异常。catch
关键字用于捕获异常。
try: try 块中的代码标识将被激活的特定异常。它后面通常跟着一个或多个
catch 块。
try { }catch ( ExceptionName e1 ) { }catch ( ExceptionName e2 ) { }catch ( ExceptionName eN ) { }
如果 try 块在不同的情境下会抛出不同的异常,这个时候可以尝试罗列多个
catch 语句,用于捕获不同类型的异常。
抛出异常
double division (int a, int b) if ( b == 0 ) { throw "Division by zero condition!" ; } return (a/b); }
捕获异常
catch 块跟在 try
块后面,用于捕获异常。您可以指定想要捕捉的异常类型,这是由 catch
关键字后的括号内的异常声明决定的.如果您想让 catch 块能够处理 try
块抛出的任何类型的异常,则必须在异常声明的括号内使用省略号
...,如下所示:
try { }catch ( ExceptionName e ) { }catch (...) { } #include <iostream> using namespace std; double division (int a, int b) if ( b == 0 ) { throw "Division by zero condition!" ; } return (a/b); } int main () int x = 50 ; int y = 0 ; double z = 0 ; try { z = division (x, y); cout << z << endl; }catch (const char * msg) { cerr << msg << endl; } return 0 ; }
由于我们抛出了一个类型为 const char*
的异常,因此,当捕获该异常时,我们必须在 catch 块中使用
const char*。当上面的代码被编译和执行时
c++标准异常
C++ 提供了一系列标准的异常,定义在
中,我们可以在程序中使用这些标准的异常。它们是以父子类层次结构组织起来的,如下所示
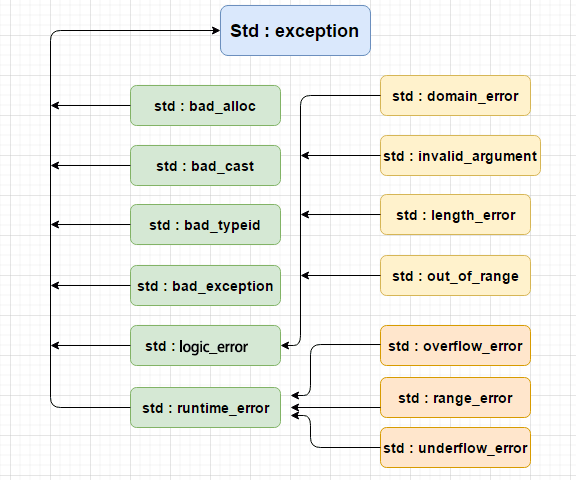
std::exception
该异常是所有标准 C++ 异常的父类。
std::bad_alloc
该异常可以通过 new 抛出。
std::bad_cast
该异常可以通过 dynamic_cast 抛出。
std::bad_exception
这在处理 C++ 程序中无法预期的异常时非常有用。
std::bad_typeid
该异常可以通过 typeid 抛出。
std::logic_error
理论上可以通过读取代码来检测到的异常。
std::domain_error
当使用了一个无效的数学域时,会抛出该异常。
std::invalid_argument
当使用了无效的参数时,会抛出该异常。
std::length_error
当创建了太长的 std::string 时,会抛出该异常。
std::out_of_range
该异常可以通过方法抛出,例如 std::vector 和
std::bitset<>::operator
std::runtime_error
理论上不可以通过读取代码来检测到的异常。
std::overflow_error
当发生数学上溢时,会抛出该异常。
std::range_error
当尝试存储超出范围的值时,会抛出该异常。
std::underflow_error
当发生数学下溢时,会抛出该异常。
定义新的异常
可以通过继承和重载 exception
类来定义新的异常。下面的实例演示了如何使用 std::exception
类来实现自己的异常:
#include <iostream> #include <exception> using namespace std; struct MyException : public exception{ const char * what () const throw () { return "C++ Exception" ; } }; int main () try { throw MyException (); } catch (MyException& e) { std::cout << "MyException caught" << std::endl; std::cout << e.what () << std::endl; } catch (std::exception& e) { } }
在这里,what()
是异常类提供的一个公共方法,它已被所有子异常类重载。这将返回异常产生的原因。